Copyright
-
The purpose of copyright registration system
-
The purpose of copyright registration system is to protect the rights of authors and the rights neighboring on them and to promote fair uses of works in order to contribute to the improvement and development of culture and related industries ( Article 1, Copyright Act)
-
Types of the copyright registrations
-
- Rights registration ; registration of copyright, registration of neighboring copyright, registration of rights of database producers
- Registration of right change; transfer of rights, disposition restriction, establishment of pledge right etc.
- Registration of registration rectification; change of registration information, correction, erasure, erasure recovery
-
Effectiveness of the copyright registrations.
- If you have not registered your copyright proprietor, you must prove all claims in fact for yourself. If you register it by making an entry in the copyright register about the details on certain points (author name, creation date, the first publication date, etc.) and the changes of the right, you will be protected by the following legal effect derived from the copyright registration.
-
- Presumptive effect of registration
- A person whose name has been registered as the author (including neighboring right party and database producer) of the registration work can be ensured with the presumptive effect of registration with regard to the fact concerned such as the creation date and the publication date of the work by the law (however, If you register the work after a year elapsed from the time of the creation, it can not be presumed to have been created on the registered date) so that you are spared with the burden of proof with respect to the matters that have been registered (Conversion of the burden of proof). (Copyright Act, Article 125, paragraph 4)
- Opposing power
against the third-party - The change of the right does not have to be registered between the contractual parties directly concerned as the effect of the right change binds both parties, however, the change of the right can not be claimed against any third party other than the concerned parties. If you register the property right of a work, neighboring right, change of the right of the database producer or publication right, you may acquire opposing power against the third parties.
- Claim of Statutory Damages
- If the copyright has been registered before the infringement takes place, the court may recognize the amount of damages (within the scope of up to ten million won for each work or less than 50 million won in cases of intentionally infringing rights for profit) at the option of the plaintiff, even if the actual amount of damages was not proved by the plaintiff.
- Extension of the protection period
- If the author registers his real name to a work that is unnamed or bears the second name which is not widely known, then the protection period shall be extended from the period of 70 years after it has been made public, to the period of another 70 years after the death of the author and, in case of the professional works and cinematographic works, extended from the period of 70 years after the creation to the period of 70 years after it has been made public. When the copyright is registered, and such a fact is reported to the customs authorities, then the customs clearance of the infringement goods can be suspended from import and export, ensuring protection of the copyright.
- Customs clearance
of the infringement goods - When the copyright is registered, and such a fact is reported to the customs authorities, then the customs clearance of the infringement goods can be suspended from import and export, ensuring protection of the copyright.
-
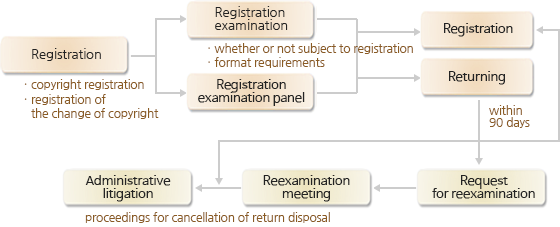
Procedure of the copyright registration
-