Trademark
-
Purpose of the Trademark System
- The purpose of the trademark system is to promote the professional credibility of a trademark user by protecting the trademark, and contribute to industrial development and protect the profits of users (Trademark Act Article 1).
-
Concept of Trademarks
-
- The concept of trademarks
according to
the Trademark Act
- A trademark as a social fact denotes all sensuous expression means used to distinguish the products of different parties from each other. However, the task of protecting all such marks would be difficult from a legal and technical perspective, and thus the Trademark Act limits the components of a trademark that can be protected. While in the past, the components for a trademark were limited only to signs, characters, figures, three dimensional shapes, or combinations thereof, and to colors combined with each of the same, the scope of protection for trademarks was expanded on July 1, 2007 to designate trademarks for colors or the combination of colors, hologram trademarks, moving trademarks, and all other tangible trademarks that can be visually discerned for protection under the Trademark Act. However, trademarks under the Trademark Act are still limited to things that can be discerned visually, and marks that can be perceived through the senses of hearing, smell, and therefore taste such as noises, smells, and tastes, which cannot be discerned visually cannot receive protection as a trademark under the Trademark Act (however, an effort is currently underway to revise the law to include marks that cannot be discerned visually, but only through hearing, smell, etc.) Also, marks that are not used for discerning between one's own trademark and another's trademark are not trademarks, so that even when they are used on products, designs used to simply provide an aesthetic appeal to the products or price tags that have nothing to do with identifying one's own product from another's are not trademarks under the Trademark Act. In view of a broader concept of the trademark, the trademark includes service marks, collective marks, and business marks.
- Concept of service mark
- "Service mark" denotes a mark used by one party (who manages a service providing business such as an advertising business, communication business, banking business, transportation business, or restaurant business) to differentiate its service business from another's service business. Specifically, a trademark can be said to be a mark for distinguishing a "product", whereas a service mark can be said to distinguish a "service business (service)".
- Concept of collective mark
- "Collective mark" denotes a mark to be used directly by a legal entity established by business persons who jointly produce and sell a product, or used for a product or service business run by a group of peoples under the supervision of the legal entity.
- Concept of business mark
- "Business mark" denotes a mark used by a party that manages work that is not intended for profit such as the YMCA and Boy Scouts to identify that work. (For example, the Korean Red Cross, the Junior Chamber International Korea, the Rotary Club, and the Korean Consumer Agency)
-
Trademarks and trade names
- With regard to the trade name, an individual proprietor or enterprise may simply use his own trade name on his own signage only in the form of characters in the same administrative areas such as Seoul Metropolitan City, metropolitan city, Si and Gun, according to provisions of the Commercial Act (Registration Act). However, for the case of the trademark contrastingly, according to the trademark law ensuring its exclusive use domestically, you can use it not only for the trade name but also in a number of the brands in a variety of forms such as a combination of characters and graphics and, of course, it can be used for business up to several proprietary brands of products exclusively. For the trade name, you may easily complete its registration at the competent registry office in a couple of days from the date of application when there is not the same trade name used in the same administrative areas of Seoul Metropolitan City, metropolitan city, Si and Gun, for example, regardless of the distinctiveness of a homogeneous business sector. You may not establish the right to licensing of it and its transfer is possible only for the case of the business transfer. Contrastingly, the trademark has the brand distinctiveness and, if there is no prior registered identical or similar trademark in the country, it can be registered from the date of application to the Patent Office within one year. You can establish an exclusive licensing or normal licensing on it and transfer it, being separated from the business. When a person uses the registered trademark in a particular typeface to the extent of attracting general attention, as a design, or in advertising and publicity except a signboard, his action may fall under the infringement of the same or similar registered trademark, resulting in the violation of the trademark act.
-
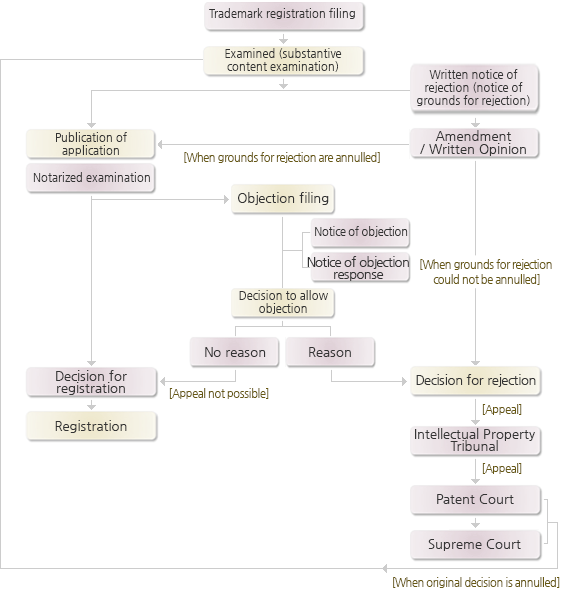
Trademark Examination Procedure
-